Direct sum of two subspace (or vector space) and is denoted by .
Say, is the resultant subspace from the direct sum. To be a valid direct sum the following two properties need to hold:
- where
Another interpretation of this definition is : can be uniquely written.
Consider two subspaces and .
Here, the subspace contains vector of the form shown below:
And, the subspace contains vector of the form shown below:
Visualization of direction sum is given below:
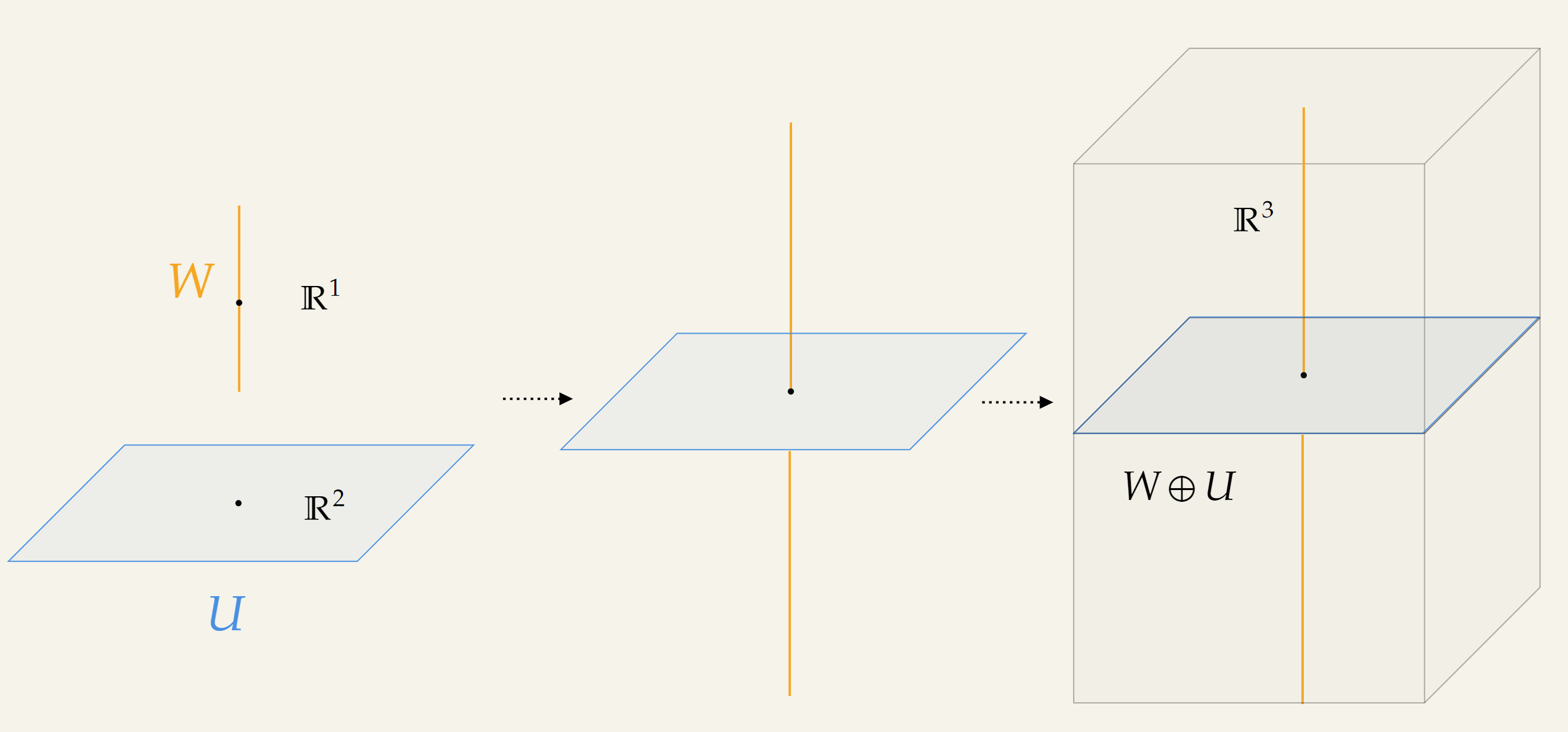 We can clearly see that, when we add and , there is only one way they can be added. And the resultant will have the following form:
We can clearly see that, when we add and , there is only one way they can be added. And the resultant will have the following form:
A counter example might provider better perspective. Consider the following:
Here, the vector can be written in infinitely different ways as the value of and changes.